How Does CPR Differ in an Unresponsive Adult Choking Victim?
TLDR;
When an adult choking victim becomes unresponsive, CPR differs by first focusing on clearing the airway before performing compressions and rescue breaths. If the airway cannot be cleared, continue chest compressions without delay until the obstruction is removed or emergency services take over.
Recognizing an Unresponsive Choking Emergency
In an emergency, identifying an unresponsive adult choking victim quickly is critical. Airway obstruction can escalate rapidly from distress to unconsciousness.
Common Signs of Airway Obstruction Before Collapse
- Inability to cough, breathe, or speak
- Clutching the throat (universal choking sign)
- Gasping sounds or complete silence
- Panic and inability to respond to questions
- Skin turning bluish (cyanosis)
Recognizing these signs early provides a vital opportunity to act before the victim collapses.
When Does a Choking Person Become Unresponsive?
A choking person becomes unresponsive when airway obstruction fully blocks oxygen flow, leading to unconsciousness. Immediate steps must shift from Heimlich maneuver attempts to CPR with airway clearance priority.
How CPR for Choking Differs from Standard CPR
Performing CPR on an unresponsive choking victim changes the approach compared to traditional cardiac arrest scenarios.
Standard CPR vs. CPR for an Airway Obstruction
- Standard CPR: Focuses on restoring heart function and breathing when cardiac arrest occurs.
- Choking-Related CPR: First priority is to clear the obstruction before focusing on circulation.
If obstruction removal is unsuccessful, proceed with continuous chest compressions without rescue breaths.
The Role of the Heimlich Maneuver Before CPR Begins
- For conscious choking adults, the Heimlich maneuver is the first line of defense.
- If the victim becomes unresponsive despite Heimlich efforts, transition immediately to CPR.
- Do not continue Heimlich maneuvers once the victim is unconscious.
Checking the Mouth for Obstructions Before Rescue Breaths
Before delivering rescue breaths:
- Open the victim’s mouth and perform a careful finger sweep.
- Only remove visible objects—do not perform blind sweeps.
- If no object is visible, attempt rescue breaths; if unsuccessful, resume compressions.
This method aligns with
step-by-step CPR instructions for an unresponsive choking victim.
Step-by-Step Guide to CPR on an Unresponsive Choking Adult
Every second matters. Here's how CPR Professionals recommends you act:
Call Emergency Medical Services (EMS) and Assess the Victim
- Check for responsiveness and breathing.
- If no response or normal breathing, call 911 immediately or ask someone nearby to call.
- Retrieve an AED if available.
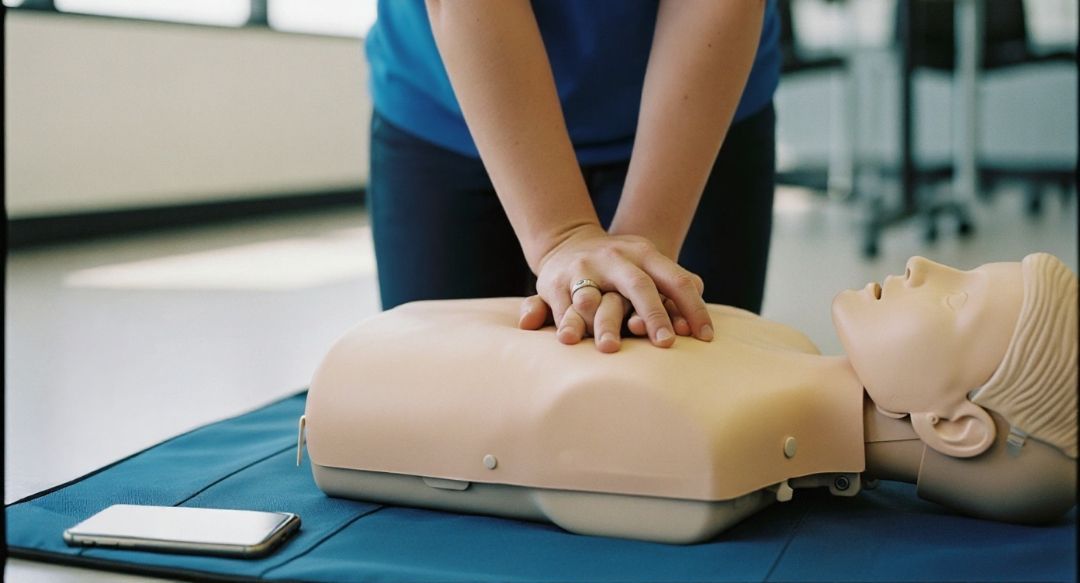
Begin Chest Compressions if No Pulse or Breathing
- Place hands at the center of the chest.
- Perform compressions at a depth of 2 inches at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute.
- Allow the chest to fully recoil between compressions.
Chest compressions may help dislodge the airway obstruction through internal pressure.
Deliver Rescue Breaths — Only if the Airway is Clear
- After 30 compressions, open the airway using the head-tilt-chin-lift maneuver.
- Look for visible obstruction.
- If clear, deliver 2 rescue breaths.
- Watch for chest rise to confirm effective ventilation.
If the chest does not rise, reposition the head and try again. If still unsuccessful, continue compressions.
Use an AED if Available
- Power on the AED immediately.
- Follow voice prompts.
- Apply pads and allow the device to analyze the rhythm.
- Shock if instructed, then resume CPR.
AEDs greatly improve survival chances in unresponsive emergencies.
Special CPR Considerations Based on Patient Type
Certain populations require adjusted techniques to improve outcomes. If you're unsure how protocols vary by age group, it's worth learning more about CPR Age Differences to ensure the right actions for every situation.
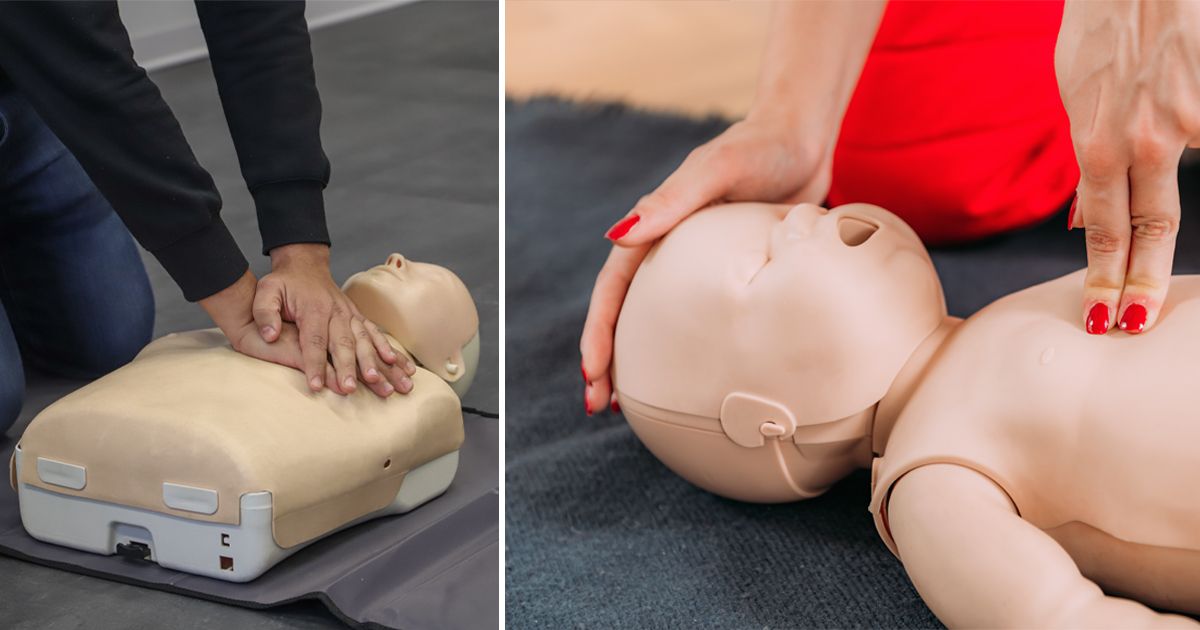
Modifying CPR for Obese or Pregnant Adults
- For obese or pregnant victims, place hands slightly higher on the sternum for compressions.
- Avoid abdominal thrusts in pregnant individuals; focus on chest thrusts instead.
These adaptations prevent further harm while maximizing effectiveness.
When to Stop CPR and Recheck the Airway
- Stop only if you can see and remove a visible obstruction.
- If breathing returns spontaneously.
- If EMS arrives and takes over.
Never discontinue compressions solely because of fatigue unless another rescuer is available.
Legal & Ethical Considerations: Are You Protected?
Bystanders often hesitate to act due to fear of legal consequences. Knowledge of Good Samaritan protections is empowering.
Understanding Your Rights During a Medical Emergency
- Good Samaritan Laws generally protect lay responders from liability when providing aid in good faith.
- Acting within your level of training shields you legally.
These laws encourage action rather than hesitation.
Good Samaritan Laws and Liability Coverage
- As long as you act reasonably and without gross negligence, you are protected.
- Always prioritize the victim’s best interests.
At CPR Professionals, we emphasize that hesitation costs lives. Legal safeguards exist to support immediate response.
Aftercare and What to Do Once CPR Succeeds (or Fails)
Your duty of care continues after initial revival efforts.
Monitoring the Victim Until Help Arrives
- Place the victim in the recovery position if breathing resumes.
- Continually reassess breathing and pulse.
- Be prepared to resume CPR if conditions worsen.
What to Do If the Victim Regains Consciousness
- Keep them calm and still.
- Do not give food or drink.
- Reassure them until EMS takes over.
Early medical intervention is crucial even after signs of recovery.
Debriefing and Self-Assessing Your CPR Performance
- Reflect on your actions post-incident.
- Identify strengths and areas for improvement.
- Seek refresher training if necessary.
Saving a life is a profound experience; reflection helps solidify skills for future emergencies.
Preventive Education and CPR Certification
Preparedness saves lives. Education is the first step.
Importance of Training in Adult Choking Scenarios
- Comprehensive
CPR training includes choking rescue techniques.
- Hands-on practice improves response speed and confidence.
CPR Professionals offers tailored classes for real-world emergencies.
How Often to Recertify for CPR
- Recertification is typically required every two years.
- Regular updates ensure alignment with evolving best practices.
Stay certified. Stay ready.